Там . 16, 2024 17:35 Back to list
Fifth Wheel Rebuild Services for Fontaine Trailers by Leading Exporter
Rebuilding the Fontaine Fifth Wheel A Guide for Exporters
The Fontaine fifth wheel is a crucial component in the trucking industry, serving as the connection between a tractor and a trailer. To maintain safety and efficiency in transportation, regular maintenance and rebuilding of these fifth wheels are essential. For exporters involved in the logistics of heavy equipment, understanding the nuances of rebuilding a Fontaine fifth wheel can significantly enhance operational effectiveness and compliance with industry standards.
Understanding the Fontaine Fifth Wheel
Fontaine fifth wheels are renowned for their durability and reliability. They are designed to facilitate smooth towing capabilities while ensuring the stability of the load. Over time, constant wear and tear can lead to performance issues, making it important for exporters to consider rebuilding these essential components periodically. This not only prolongs the life of the fifth wheel but also ensures that trucking fleets remain compliant with safety regulations.
The Importance of Rebuilding
Rebuilding a Fontaine fifth wheel involves disassembling the unit, inspecting each component, and replacing any worn or damaged parts. This process is vital for several reasons
1. Safety Compliance Regular maintenance ensures compliance with safety regulations. A well-maintained fifth wheel reduces the risk of accidents caused by equipment failure, ultimately protecting the driver and other road users.
2. Cost-Effectiveness While the initial investment in rebuilding may seem high, it is often more cost-effective than purchasing a new unit. By extending the lifespan of existing equipment, companies can save money on replacements.
3. Enhanced Performance A rebuilt fifth wheel operates more efficiently, improving fuel economy and overall performance of the truck-trailer combination. This efficiency can translate into significant savings over time.
The Rebuilding Process
The rebuilding process should be conducted by skilled technicians familiar with Fontaine products. Here's a general outline of the steps involved in rebuilding a fifth wheel
1. Disassembly The first step involves safely removing the fifth wheel from the truck and disassembling it. This is critical for thorough inspection.
fontaine fifth wheel rebuild exporter
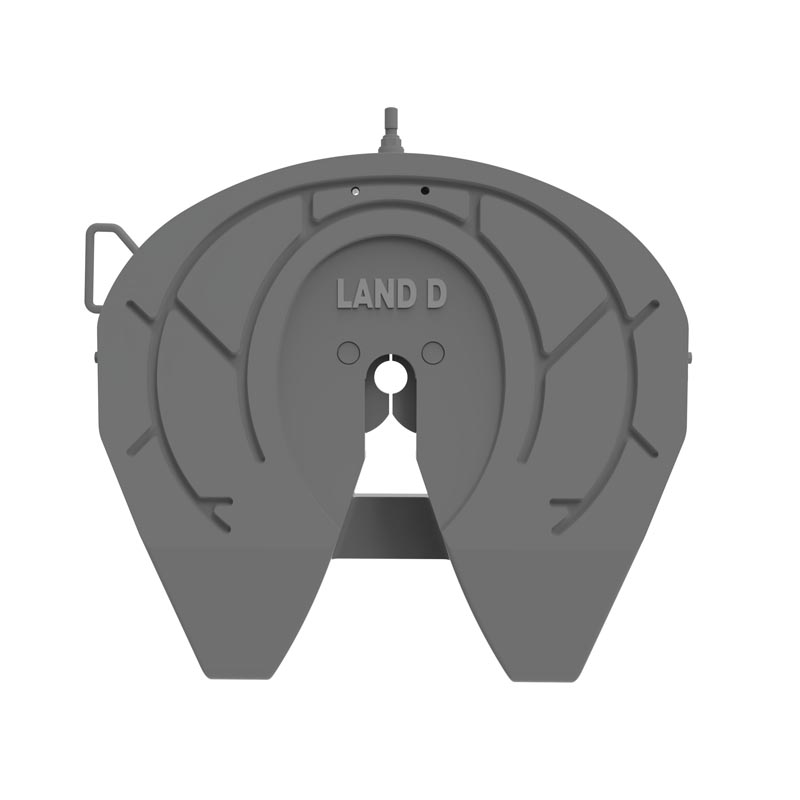
2. Inspection Each component, including the kingpin, locking mechanism, and pivot points, must be inspected for wear and damage. Any issues should be documented for reference.
3. Replacing Parts Based on the inspection, necessary parts should be replaced with genuine Fontaine components to ensure compatibility and reliability. This is crucial to maintaining the integrity of the fifth wheel.
4. Reassembly Once all components are inspected and repaired, the fifth wheel is reassembled, ensuring that all mechanical and safety features function correctly.
5. Testing After reassembly, thorough testing is imperative. This includes checking for proper alignment, movement, and functional locking mechanisms.
Best Practices for Exporters
For exporters dealing with the logistics of heavy machinery and parts, keeping these best practices in mind can streamline operations
- Documentation Maintain thorough records of maintenance and rebuilding activities. This is essential for warranty purposes and can be beneficial during audits.
- Training Invest in training for technicians on the latest rebuilding techniques and safety standards. This can improve the quality of work and enhance overall safety.
- Supplier Relationships Develop strong relationships with suppliers of genuine Fontaine parts. This ensures quick access to high-quality components necessary for effective rebuilds.
- Regular Maintenance Schedules Implement a proactive maintenance schedule for all fifth wheels in your fleet, reducing the risk of unexpected failures.
Conclusion
Rebuilding Fontaine fifth wheels is a crucial aspect of maintaining a reliable and safe trucking operation. By understanding the rebuilding process, adhering to best practices, and prioritizing safety and efficiency, exporters can ensure that their equipment remains in optimal condition. This commitment not only enhances operational effectiveness but also contributes positively to the safety and sustainability of the logistics industry as a whole.
-
Imperial Truck Repair Hayward CA - High Quality, Affordable & Reliable Services
NewsJun.10,2025
-
High Quality Fontaine International do Brasil – Best Discount Offers Online
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Premium Fontaine Valves - High Quality & Discount Offers Durable
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Premium Fifth Wheel King Pins Top Durability & Savings
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Best Semi Trailer Kingpins for Sale Premium & Discounted
NewsJun.10,2025
-
Premium Holland Fifth Wheel Slider Parts Durable & Discount Deals
NewsJun.09,2025
