Oct . 16, 2025 14:21 Back to list
Germany Type Suspension – DIN-Compliant, High-Strength Clamp
Inside the German‑type trailer suspension trend: what really matters
If you work around trailers long enough, you hear the same question: why are fleets switching to the Germany Type Suspension architecture for axles and hangers? Short answer: durability under heavy loads and nicer tire wear. Longer answer: well, that’s what we’re getting into here.
Origin-wise, this unit comes out of Shijiazhuang City, Hebei Province, China. I visited suppliers in that region a few years ago; the welding lines have become surprisingly automated. And yes, you can feel the influence of classic German layout—wide track, robust spring stacks, predictable roll control.
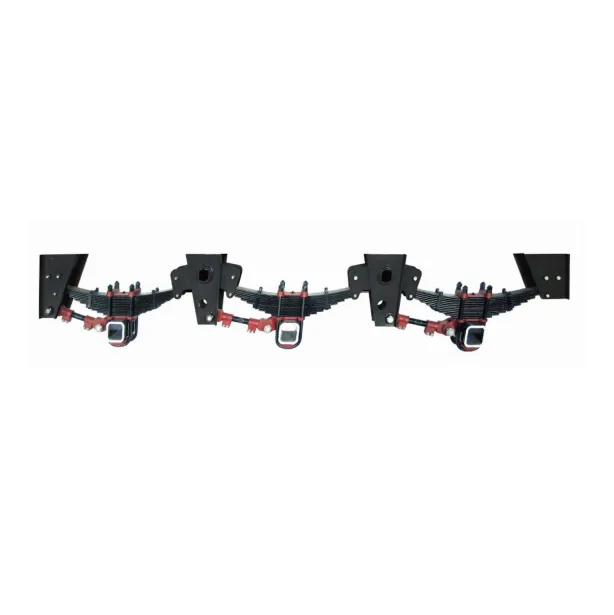

Where it’s used (and why operators pick it)
Common applications: flatbeds, tippers, tankers, container chassis—plus a few lowbeds. Many customers say the Germany Type Suspension feels “forgiving” on mixed roads, with consistent ride height and decent brake response. In fact, compared with some lightweight sets, tire edge wear seems reduced—anecdotal, yes, but I keep hearing it.
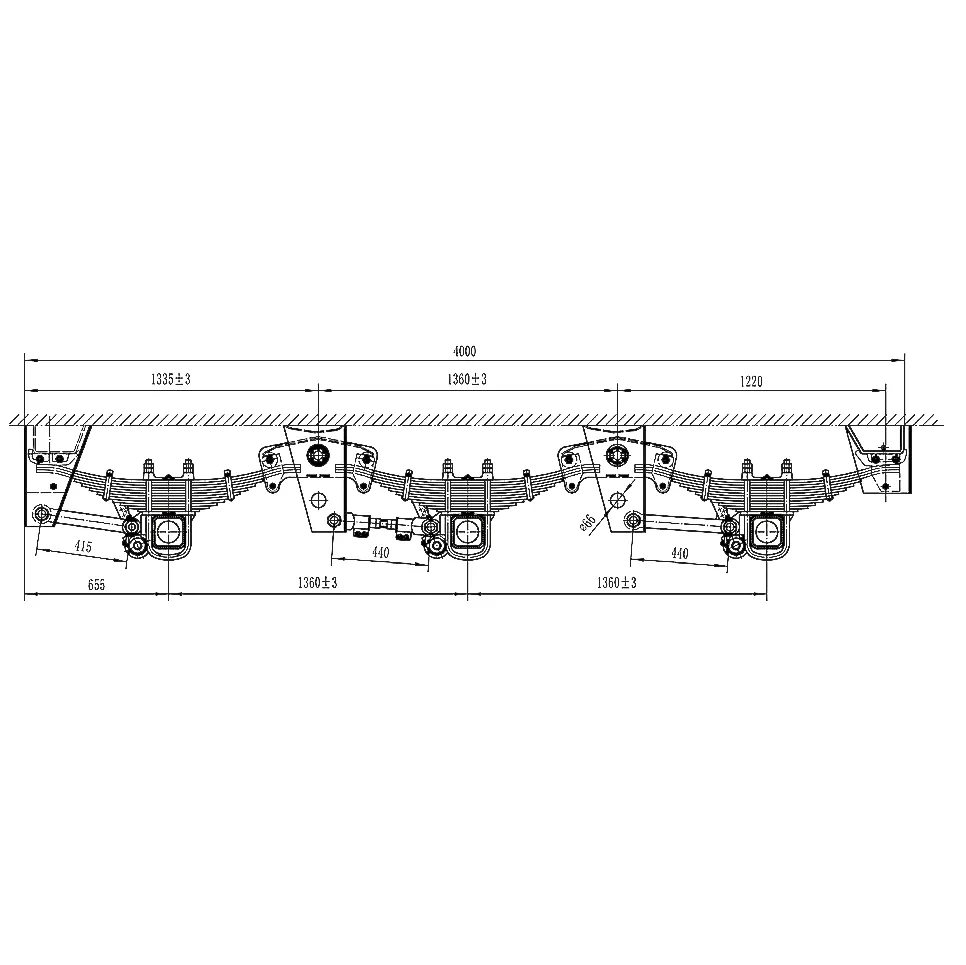
Key specifications (typical build, configurable)
| Parameter | Spec (≈/range; real-world use may vary) |
|---|---|
| Axle load rating | 13T / 16T / 20T options |
| Track width | ≈ 1810–2010 mm |
| Hanger spacing | ≈ 930–980 mm |
| Spring pack | Multi‑leaf 90 mm or 100 mm width; shot‑peened |
| Brake size | Drum 420×180 mm (disc optional) |
| Materials | Q345B/EN 10025 structural steel; 42CrMo pins/bushings |
| Surface treatment | Phosphate + powder coat (salt spray ≥ 240 h per ISO 9227) |
| Service life | ≈ 8–10 years or 800k–1M km with proper maintenance |
| Operating temp | −30 °C to +60 °C |
Process flow (how it’s built)
Materials are selected to DIN/EN standards; hangers and brackets are laser‑cut, then robotic welded (MAG). Leaf springs get shot‑peened and tempered to stabilize residual stresses. After phosphating, parts are powder‑coated; hardware is zinc‑nickel plated. Testing includes weld macro‑etch checks, hardness (HRC on pins), axial fatigue (≥ 2×106 cycles target), salt spray to ISO 9227, and road‑simulation rig tests aligned with ECE R13 brake performance.
What fleets report
“Tire scrub went down after switching,” a Baltic fleet manager told me. Another customer in the Gulf noted better heat resistance on bushings—though he added, to be honest, road cleanliness helped. Overall, feedback on the Germany Type Suspension leans positive for stability and maintenance intervals.
Vendor comparison (quick snapshot)
| Vendor | Certs | Lead time | Warranty | Customization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Fifth Wheel (Hebei) | ISO 9001; tests to ISO 9227/ECE R13 | ≈ 20–35 days | 12–24 months (region‑dependent) | Track, hanger spacing, paint, brake options |
| Generic Importer A | Basic QA docs | ≈ 30–45 days | 6–12 months | Limited SKU tweaks |
| European OEM | IATF 16949; ECE component approvals | ≈ 6–10 weeks | 24–36 months | Extensive, but higher cost |
Customization and integration
Options include air‑ride interfaces, disc brake packages, ABS/EBS readiness, hanger geometry tweaks, and corrosion upgrades (C3→C4). For multi‑axle sets, equalizer tuning and bush material (NBR vs. PU) can be specified. I guess the practical advice: match track and brake size to tire and regional regulations first—everything else follows.
Mini case notes
- Germany heavy‑haul: 16T spec, drum 420×180; 2.2×106 fatigue cycles on rig; tire wear down ≈ 7% over 12 months vs previous spec.
- Middle East tanker: added anti‑corrosion topcoat and PU bushings; uptime improved through a harsh summer (operator feedback).
Bottom line: a well‑built Germany Type Suspension is still about fundamentals—steel quality, weld integrity, and honest testing—more than buzzwords.
Authoritative standards and references
- EN 10025: Hot rolled products of structural steels (material selection guidance).
- ISO 9227: Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres — Salt spray tests.
- ECE R13: Uniform provisions concerning the approval of vehicles with regard to braking.
- ISO 9001: Quality management systems — Requirements (manufacturing QMS).
-
Fontaine No Slack II Adjustment: Enhancing Trailer Suspension Reliability & Safety
NewsNov.25,2025
-
Fontaine PDF Explained: Industrial Documentation, Specs & Innovation
NewsNov.24,2025
-
Heavy Haul Fifth Wheel – Essential Couplers for Oversized Transport
NewsNov.24,2025
-
Comprehensive Guide to Parts of the Fifth Wheel | Essential Components & Innovations
NewsNov.23,2025
-
Comprehensive Guide to 5th Wheel Parts: Key Components, Vendors & Future Trends
NewsNov.23,2025
-
Comprehensive Guide to Fifth Wheel Grease: Lubrication for Safety and Efficiency
NewsNov.22,2025
